The kinematics of continuum decay reactions is derived from that for
continuum two-body reactions. The difference is that the initial
unstable nucleus plays the rôle of the incident particle, and the
target is null. This unstable nucleus may now be in an excited state,
either because the previous reaction was inelastic scattering to some
excitation level or because we had a continuum reaction leading to an
average excitation as given by (24). Note that the
reactions discussed here include those like
(n, 2n![]() ), in which
there is more than one secondary particle of the same kind. The
special considerations required for such reactions are spelled out at
the end of this section.
), in which
there is more than one secondary particle of the same kind. The
special considerations required for such reactions are spelled out at
the end of this section.
Let us introduce the notation that
mprev denotes the mass of the
initial unstable nucleus and that
Eprev and
Wprev are,
respectively, its kinetic energy and excitation level. We again use
the integral (16) to calculate the average energy
![]() Eyo
Eyo![]() of the secondary particle emitted at this
stage.
of the secondary particle emitted at this
stage.
As with continuum 2-body reactions, the calculation of the average kinetic energy of the final residual depends on whether or not gamma energy distributions are given. If they are given, then the average gamma energy is obtained from the integral (16), and energy balance is used to determine the average energy of the stable residual nucleus. Likewise, if the residual is an alpha or lighter, we assume that there is no gamma emission, and the average kinetic energy of the residual is obained from energy balance.
If gamma energy distributions are not given and if the residual is heavier than an alpha, then as in Section 3.1 we use the reaction kinematics to determine the average kinetic energy and excitation level for the residual at each step of the decay process. Thus, for one decay step the mass ratios (18) take the form
The equation for the average excitation level of the residual (24) simplifies to
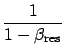 {
{
What we do if the computed value of
![]() Wres
Wres![]() comes out
to be negative depends upon whether or not this is the final decay
step. If this is the final decay process and the computed value of
comes out
to be negative depends upon whether or not this is the final decay
step. If this is the final decay process and the computed value of
![]() Wres
Wres![]() is negative, we replace it by zero and print a
warning message. For intermediate decay steps we keep the negative
average excitation and print a warning to indicate that the model may
be wrong and that the decay steps probably ought to be done in a
different order.
is negative, we replace it by zero and print a
warning message. For intermediate decay steps we keep the negative
average excitation and print a warning to indicate that the model may
be wrong and that the decay steps probably ought to be done in a
different order.
The equation (25) for the average kinetic energy of the residual becomes