


Next: Interpolation
Up: Various identifiers
Previous: The I_number identifier of
Contents
Kinematics types
The reactions are classified into 8 different types, depending on the
data present in the library. These are called kinematics types,
because the classification is related to the kinematics of the
reactions. Cross sections are given in all cases. The different
kinematics types are as follows, along with a description of the
additional data provided.
- Kinematics type 0:
- Only cross sections are given.
- Kinematics type 1:
- This kind of data describes 2-body
interactions in center-of-mass coordinates. The library provides
angular distributions (
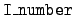 = 1 data) and energy
deposition to the secondary particle (
= 1 data) and energy
deposition to the secondary particle (
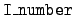 = 10
data). Energy distributions for the secondary particle are not
given, because they are easily derived. In fact, the mcfgen
code identifies this kinematics type by a lack of energy
distribution data (
= 10
data). Energy distributions for the secondary particle are not
given, because they are easily derived. In fact, the mcfgen
code identifies this kinematics type by a lack of energy
distribution data (
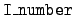 = 4). In addition, if the
residual nucleus is light enough to be viewed as a particle (an
alpha-particle or lighter), energy deposition to it is provided.
= 4). In addition, if the
residual nucleus is light enough to be viewed as a particle (an
alpha-particle or lighter), energy deposition to it is provided.
- Kinematics type 2:
- Usually, this kinematics type refers to
reactions with more than two final particles, but it also applies
to capture reactions
(yi,
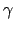 ). With one exception, energy
distributions (
). With one exception, energy
distributions (
 = 4 data) are given only for the
first secondary particle. The exception is that
(yi, pn'
= 4 data) are given only for the
first secondary particle. The exception is that
(yi, pn'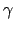 ) reactions with excited residual are classified as
kinematics type 4, irrespective of what energy distributions are
given. Angular distributions may also be included. The angular
data is independent of the energy distributions, and it is given
in the laboratory system.
) reactions with excited residual are classified as
kinematics type 4, irrespective of what energy distributions are
given. Angular distributions may also be included. The angular
data is independent of the energy distributions, and it is given
in the laboratory system.
- Kinematics type 3:
- This kinematics type applies to the case
when joint distributions in angle and secondary energy (both
 = 1 and
= 1 and
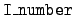 = 3 data) are given.
= 3 data) are given.
- Kinematics type 4:
- For this kinematics type we start with a
2-body reaction in center-of-mass coordinates, but one of the
products is an unstable intermediate nucleus which decays with
type-2 kinematics. Most of these reactions are identified by the
presence in the library of energy distribution data (
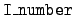 = 4) for a secondary particle which is not the first.
The exception to this rule is that
(yi, pn'
= 4) for a secondary particle which is not the first.
The exception to this rule is that
(yi, pn' ) reactions
with an excited residual are automatically given kinematics
type 4.
) reactions
with an excited residual are automatically given kinematics
type 4.
- Kinematics type 5:
- This is a very special case which is
currently used only for the reaction d (n, n')np. We start with a
2-body reaction in center-of-mass coordinates, with sufficient
energy to break up the deuteron. The neutron and proton resulting
from the break-up of the deuteron simply go off independently at
the velocity of the unstable recoil deuteron.
- Kinematics type 6:
- In this special case the data consists of
form factors for coherent (Rayleigh) scattering of a photon
(
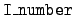 = 941).
= 941).
- Kinematics type 7:
- In this special case the data consists of
form factors for incoherent (Compton) scattering of a photon
(
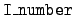 = 942).
= 942).
The subroutine models in mcfgen determines the kinematics
type, based on the information given above.



Next: Interpolation Up: Various identifiers Previous: The I_number identifier of Contents